Summary
Physical Description
Ecology
Habitat
Symbioses
Life History and Behaviour
Reproduction
Development
Feeding
Mobility
Anatomy & Physiology
Internal Morphology
Respiration
Toxins
Biolfluorescence
Evolution & Systematics
Biogeographic Distribution
Conservation & Threats
References & Links |
Anatomy & Physiology
The internal morphology of E. quadricolor is consistent with that of other Anthozoa and follows a body plan common among small invertebrates. However, this species is interesting physiologically with the presence of toxins and fluorescent compounds including a uniquely far-red shifted red fluorescent protein (RFP). More detailed information on such topics is provided in the following pages.
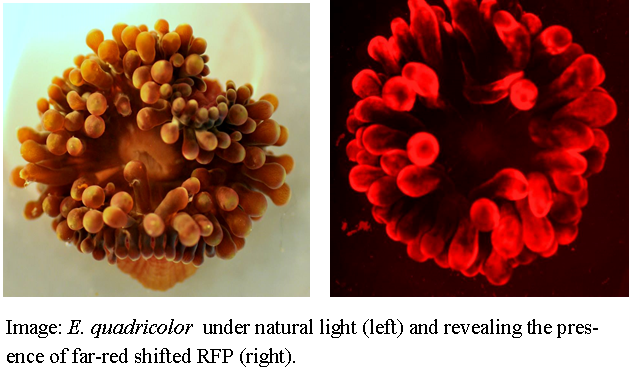
|
|